Nervous system
Nerves:
Neurons bundle together to form nerves
They are pathways that transmit electrochemical signals from one part of the body to another.
Neurons:
They are cells that receive and conduct impulses.
There are 2 ways to classify neurons:
1.Into sensory, motor and Interneurons
Sensory neurons:
Neurons which carry information form the sensory organs
Interneurons
Neurons which connect neurons to other neurons within the same part of brain or spinal cord
Motor neurons:
Neurons which are responsible for carrying information from the brain or spinal cord to the rest of body
2.Into afferent and efferent:
Afferent neurons:
Afferent means to carry things to a central point
Afferent neurons carry information to the brain and spinal cord
In the peripheral nervous system, afferent neurons are the sensory neurons
In the central nervous system, afferent neurons bring information to specific parts of the brain
Efferent neurons:
Efferent means to carry things away from a central point
Efferent neurons carry information from the brain and spinal cord
In the peripheral nervous system, efferent neurons are the motor neurons
In the central nervous system, efferent neurons carry information from parts of the brain to other parts of the brain
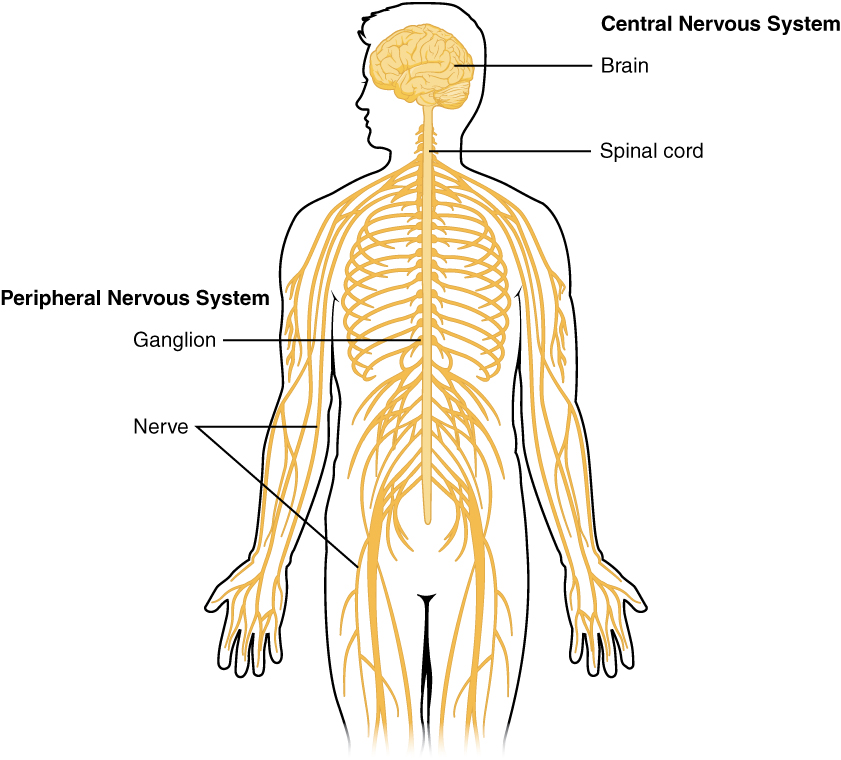
Central nervous system:
Consists of mainly the brain and the spinal cord
Analyses and interprets data from the peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system:
Consists of the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
It sends signals to other parts of the body telling them what to do
It is divided into the somatic and the autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system:
Somatic nervous system is responsible for conscious actions
Autonomic nervous system:
It is responsible for actions that you do without thinking about it
Ex: Breathing
It is divided into the sympathetic, parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system:
Responsible for fight or flight response.
It prepares for action by:
- Increasing the heart rate and blood pressure
- Enhancing the sense of smell
- Dilating the pupils
- Shutting down blood supply to the digestive and reproductive systems
- Activating the adrenal cortex which makes adrenaline
Parasympathetic nervous system:
Responsible for "rest and digest" & "feed and breed" responses that occur when the body is at rest
It can:
- Slows the heart rate and blood pressure
- Constrict the lungs
- Make the nose run
- Increases blood flow to the reproductive systems
- Increases saliva production
- Encourages defecation and urination
Together the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems maintain homeostasisState of steady internal physical and chemical condition
Enteric nervous system:
Responsible for the governing the function of the GI tract.
It operates independently of the brain and spinal cord.
It can also co-ordinate reflexes with the help of the autonomous nervous system.
Reflex actions:
Involuntary and near instantaneous action in response to a stimulus
Information reaches the spinal cord and decision is made by it, instead of the brain
The path taken by a reflex signal is called the reflex arc or the reflex loop
Structure of a neuron:
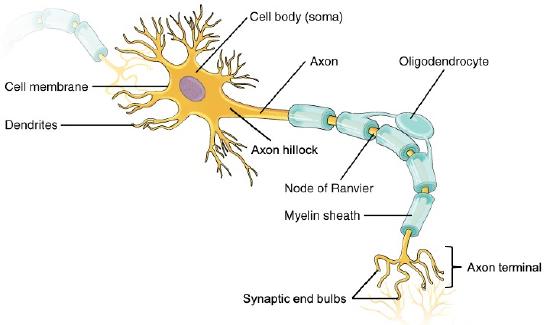
It consists of branches called dendrites which receive information from other neurons
They have a single axon which is long and has branches at the end to transmit signals to other neurons
The axon is covered in a fatty material called myelin that form the myelin sheath, they help to insulate the neuron
The myelin sheath has gaps in it called the nodes of Ranvier
The nodes help the signal travel faster by allowing it to hop from node to node
The node hoping is called saltatory conduction
The place where an axons branch gets very close to the dendrites of another neuron is called a synapse
Neurotransmitters pass information from one neuron to the next by jumping the synaptic cleft
Membrane potential:
Difference in voltage between the inside and outside of a membrane
When a neuron is inactive then its membrane potential is -70mV and is called its resting potential
Ion channels:
Along with sodium-potassium pumps, neurons also have channel proteins for ions called ion channels
Each cell can have upwards of 200 ion channels.
Working of a neuron:
When a stimulus creates a change in a neuron reaching the axon, an action potentialBrief event where electric potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls is generated.
When an action potential begins, some sodium ion channels open and sodium ions rush in making the inside less negative.
When there is enough stimulus, the internal charge of the neuron reaches a threshold and more sodium ion channels open
The change in voltage creeps over to the next bunch of channels and they open causing the next batch to open and so on
The action potential commits saltatory conduction and reaches the next node until it reaches the end
At the end, release of neurotransmitters occurs and cause an action potential in the next neuron
By the time this happens, the rush of sodium ions in the first neuron causes the membrane potential to turn positive
This then causes the sodium channels to close and potassium channels to open and potassium rushes out until the membrane potential is negative
The sodium ends up inside the cell instead of outside and potassium outside instead of inside.
This causes sodium-potassium pumps to start to pump out the sodium and pump in the potassium until the resting potential is reached




